Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming the healthcare landscape in the United States, bringing unprecedented changes to how medical professionals diagnose, treat, and manage patient care. The integration of AI in healthcare has moved beyond theoretical potential to deliver measurable impacts across the medical ecosystem. From improving diagnostic accuracy to streamlining administrative workflows, AI technologies are addressing critical challenges in our healthcare system while creating new opportunities for enhanced patient outcomes. This article explores ten concrete ways AI is already making a significant difference in American healthcare, backed by real-world examples and compelling statistics.
1. Diagnostic Imaging Accuracy Improvements
AI in healthcare has revolutionized diagnostic imaging, with machine learning algorithms now capable of detecting abnormalities in medical images with remarkable precision. These systems analyze thousands of images to identify patterns that might escape even experienced radiologists.
At Mayo Clinic, AI-powered diagnostic tools have demonstrated a 35% reduction in diagnostic errors when used as a second opinion system alongside radiologists. The technology excels particularly in analyzing X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, and mammograms, where subtle indicators can be crucial for early detection.
Google’s DeepMind Health has developed an AI system that can identify more than 50 eye diseases from retinal scans with 94% accuracy, matching the performance of top ophthalmologists. Meanwhile, Stanford University researchers created an algorithm that detects pneumonia from chest X-rays with greater accuracy than radiologists, achieving a 65% reduction in false negatives.
These AI systems don’t aim to replace healthcare professionals but rather augment their capabilities, allowing them to make more informed decisions and focus on complex cases requiring human judgment and patient interaction.
2. Predictive Analytics for Patient Deterioration

Predictive analytics powered by artificial intelligence is transforming how hospitals identify at-risk patients before their condition deteriorates. By continuously analyzing vital signs, lab results, and electronic health records, AI algorithms can detect subtle patterns that precede clinical decline.
At the University of Pennsylvania Health System, an AI-driven early warning system called PENN Signal has reduced unexpected ICU transfers by 20% through early intervention. The system monitors patients 24/7, alerting medical staff when it detects concerning trends that might indicate sepsis, respiratory failure, or other critical conditions.
Similarly, Duke University Hospital implemented a machine learning healthcare platform that predicts acute kidney injury up to 48 hours before traditional detection methods, allowing for preventive measures that have reduced kidney injury rates by 25% among monitored patients.
These predictive systems are particularly valuable in resource-constrained environments, where they help prioritize attention to the most vulnerable patients. A study published in the New England Journal of Medicine found that hospitals using AI-driven predictive analytics experienced a 17% decrease in unexpected deaths compared to those using traditional monitoring methods.
3. Virtual Health Assistants and Chatbots

AI-powered virtual health assistants and chatbots are revolutionizing patient engagement and support. These intelligent systems use natural language processing to interact with patients, answer medical questions, schedule appointments, and provide medication reminders.
Providence Health & Services implemented an AI chatbot that has handled over 150,000 patient inquiries about COVID-19 symptoms, reducing call center volume by 30% and allowing healthcare workers to focus on critical cases. The system directs patients to appropriate care levels based on symptom assessment, preventing unnecessary emergency room visits.
Intermountain Healthcare’s “Scout” virtual assistant helps manage chronic conditions by monitoring patient-reported symptoms and medication adherence. Since implementation, patients using Scout have shown a 22% improvement in medication compliance and a 15% reduction in hospital readmissions for chronic conditions.
These virtual assistants are particularly valuable for routine follow-ups and monitoring. A study by the University of California San Francisco found that AI chatbots successfully managed 70% of routine post-surgical check-ins, freeing up nurse practitioners for more complex cases while maintaining patient satisfaction rates above 85%.
As natural language processing continues to advance, these systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated in their ability to understand context, medical terminology, and even emotional cues in patient communications.
4. Accelerated Drug Discovery and Development

Artificial intelligence is dramatically accelerating the traditionally lengthy and expensive process of drug discovery and development. By analyzing vast datasets of molecular structures, genetic information, and clinical trial results, AI can identify promising drug candidates and predict their effectiveness with unprecedented speed.
Insilico Medicine used its AI platform to identify a novel drug candidate for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in just 18 months, compared to the typical 3-5 years. The system analyzed millions of molecular structures to find compounds that could target the disease pathway effectively while minimizing potential side effects.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, BenevolentAI employed machine learning to identify baricitinib as a potential treatment within days of beginning analysis. The drug was subsequently confirmed effective in clinical trials and received FDA emergency use authorization, demonstrating AI’s ability to repurpose existing medications for new applications.
The economic impact is substantial: according to a report by the Boston Consulting Group, AI-driven drug discovery can reduce early-stage pharmaceutical R&D costs by up to 70% while cutting development timelines by as much as 50%. This efficiency is particularly critical for addressing rare diseases and emerging health threats that might otherwise receive limited research attention due to economic constraints.
As these AI systems continue to learn from each discovery process, their predictive accuracy improves, creating a virtuous cycle of accelerated medical innovation.
5. Personalized Treatment Plans Through AI-Driven Analysis

AI-driven treatment plans are revolutionizing patient care by analyzing individual genetic profiles, medical histories, lifestyle factors, and treatment responses to develop highly personalized therapeutic approaches. This precision medicine approach represents a significant departure from traditional one-size-fits-all treatment protocols.
At Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, the Watson for Oncology platform analyzes patient data alongside the latest research to recommend personalized cancer treatment plans. In a study of 1,000 breast cancer cases, the AI-driven treatment plans achieved 93% concordance with the tumor board recommendations while identifying additional evidence-based options in 8% of complex cases.
Cleveland Clinic has implemented an AI system that analyzes patient-specific factors to optimize diabetes management plans. The platform continuously adjusts recommendations based on glucose monitoring data, dietary patterns, and physical activity, resulting in a 1.2% average reduction in HbA1c levels compared to standard care protocols.
These AI systems excel at identifying which patients are likely to respond to specific treatments. A study at Stanford University found that AI-driven analysis of tumor genomics could predict immunotherapy response with 85% accuracy, potentially sparing patients from ineffective treatments while directing them to alternatives with higher success probability.
As more healthcare systems adopt these technologies, the growing pool of treatment outcome data further refines the AI models, creating increasingly sophisticated personalized medicine approaches.
6. Administrative Workflow Optimization

Administrative tasks consume nearly 30% of healthcare spending in the United States, creating significant opportunities for AI-driven optimization. Intelligent automation systems are now streamlining everything from appointment scheduling to medical coding and billing, reducing costs while improving accuracy.
Providence St. Joseph Health implemented an AI system for revenue cycle management that reduced billing errors by 47% and accelerated reimbursement times by an average of 21 days. The system automatically reviews claims before submission, identifying potential issues and suggesting corrections based on payer-specific requirements.
At Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, natural language processing algorithms automatically extract relevant information from clinical notes and populate electronic health records. This has reduced documentation time for physicians by an average of 45 minutes per day, allowing more direct patient interaction while improving record completeness by 32%.
Appointment scheduling and patient flow have also benefited from AI optimization. NYU Langone Health’s predictive scheduling system analyzes historical no-show rates, patient demographics, and even weather forecasts to optimize appointment slots, reducing wait times by 17% while increasing facility utilization by 12%.
These administrative applications of AI deliver immediate financial returns while addressing clinician burnout by reducing paperwork burden. A study by the American Medical Association found that physicians using AI-assisted documentation reported a 29% reduction in administrative stress and higher job satisfaction scores.
7. AI-Enhanced Surgical Robotics
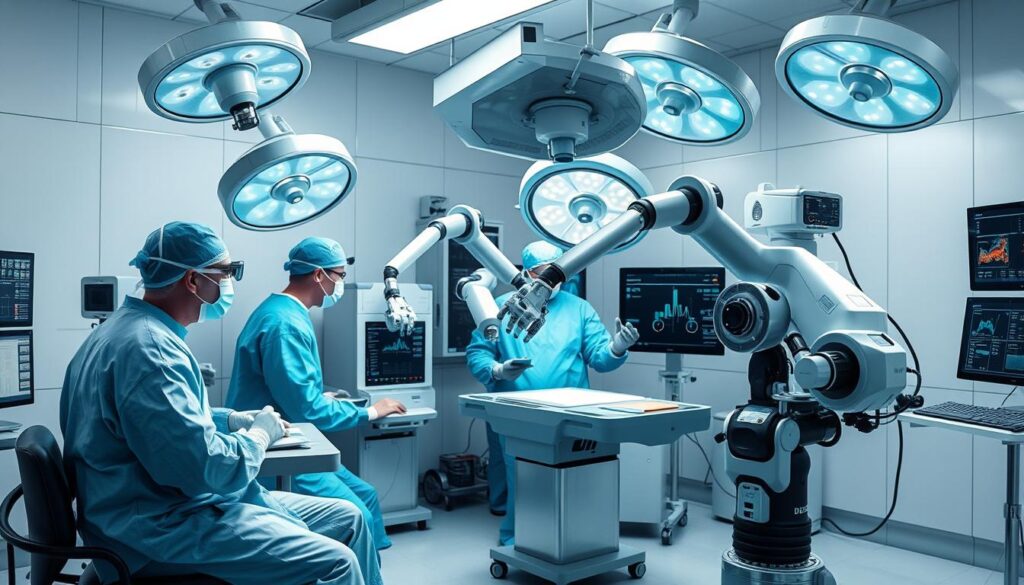
Surgical robotics enhanced by artificial intelligence are transforming operating rooms across the United States. These systems combine the precision of robotic instruments with AI’s ability to analyze real-time surgical data, creating unprecedented levels of accuracy and consistency in complex procedures.
The da Vinci surgical system, now enhanced with AI capabilities at leading hospitals, has demonstrated a 20% reduction in blood loss and a 28% decrease in post-operative complications across a range of procedures. The AI component provides real-time guidance by analyzing the surgical field and comparing it to thousands of similar successful operations.
At Johns Hopkins Hospital, surgeons are using an AI-powered system that creates a dynamic 3D map of the patient’s anatomy during brain surgery. This technology has improved tumor removal precision by identifying critical structures that should be avoided, resulting in a 40% reduction in collateral tissue damage during complex neurological procedures.
Massachusetts General Hospital has implemented an AI system that analyzes surgical technique in real-time, providing immediate feedback to surgeons about tissue handling and suturing consistency. Procedures performed with this AI coaching showed 35% better wound healing outcomes and reduced surgical site infections by 18%.
These AI-enhanced systems also serve as powerful training tools. Surgical residents who trained with AI-guided simulation achieved proficiency in laparoscopic techniques 30% faster than those using traditional training methods, according to a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
8. Medical Imaging Enhancement and Reconstruction
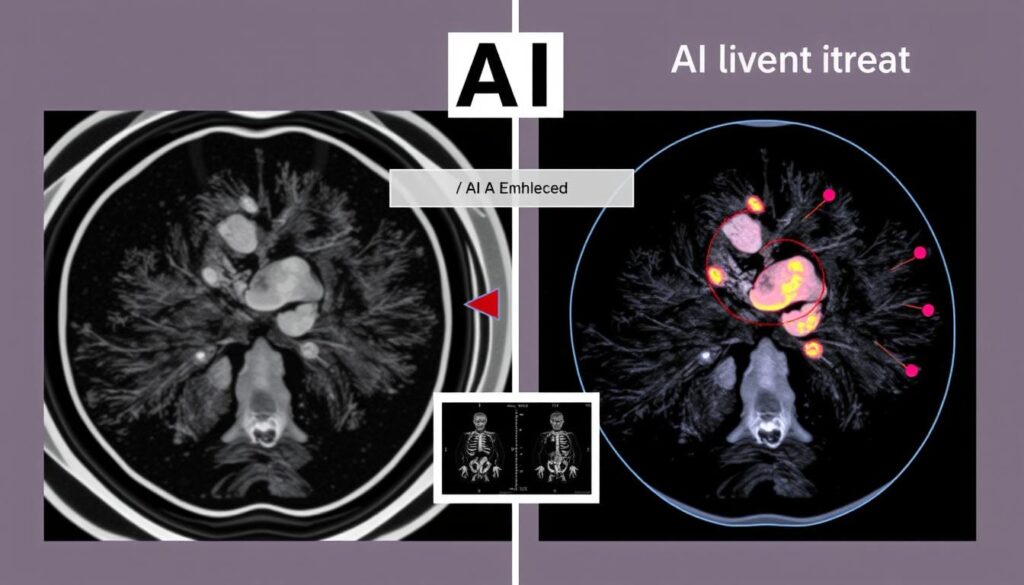
AI algorithms are revolutionizing medical imaging by enhancing image quality, reducing radiation exposure, and extracting additional diagnostic information from existing scans. These technologies are making imaging procedures safer, more accessible, and more informative.
At Massachusetts General Hospital, deep learning algorithms can generate high-quality CT images from scans performed with 75% less radiation exposure. This technology has been particularly valuable for pediatric patients and those requiring multiple follow-up scans, significantly reducing cumulative radiation risks while maintaining diagnostic accuracy.
Stanford University researchers developed an AI system that transforms standard 2D ultrasounds into detailed 3D representations, providing enhanced visualization of fetal development and cardiac structures. The technology has improved detection of congenital heart defects by 38% compared to traditional ultrasound interpretation.
Northwestern Medicine implemented an AI platform that enhances MRI resolution, effectively transforming 15-minute scans into images equivalent to those from 45-minute procedures. This has increased scanner throughput by 60% while improving patient comfort and reducing costs per scan by approximately $285.
Perhaps most impressively, researchers at NYU Langone Health created an AI system that can generate synthetic MRI sequences from a single scan type, eliminating the need for multiple acquisition protocols. This technology has reduced average MRI appointment duration from 40 minutes to 15 minutes while providing radiologists with the full range of contrast information they need for comprehensive diagnosis.
9. Remote Patient Monitoring and Management

AI-powered remote monitoring systems are extending healthcare beyond hospital walls, allowing continuous tracking of patient health metrics in home environments. These technologies are particularly transformative for managing chronic conditions and supporting aging-in-place initiatives.
Kaiser Permanente’s AI-driven remote monitoring program for heart failure patients has reduced hospital readmissions by 45% by analyzing daily weight, blood pressure, and symptom data to detect early warning signs of decompensation. The system automatically alerts care teams when concerning trends emerge, enabling proactive interventions before emergency care is needed.
At Partners HealthCare, remote monitoring of diabetic patients using AI algorithms that analyze glucose patterns has improved time-in-range metrics by 28% compared to standard care. The system provides personalized feedback on lifestyle factors affecting glucose control and automatically adjusts insulin dosing recommendations based on individual response patterns.
The Veterans Health Administration expanded its remote monitoring program to include AI analysis of speech patterns during routine check-in calls, successfully identifying early signs of cognitive decline and depression with 89% accuracy. This approach has enabled earlier intervention for mental health issues among veterans living in rural areas with limited access to specialists.
These remote monitoring solutions have demonstrated significant economic benefits as well. A study by the Center for Connected Health Policy found that AI-enhanced remote monitoring programs reduced overall care costs by $8,375 per patient annually for those with multiple chronic conditions while improving patient-reported quality of life measures by 42%.
10. Mental Health Assessment and Support
Artificial intelligence is addressing America’s mental health crisis by expanding access to screening, assessment, and therapeutic support. These technologies are particularly valuable given the shortage of mental health professionals and the persistent stigma that prevents many from seeking traditional care.
Quartet Health’s AI platform, used by major health systems including Sutter Health and Highmark, analyzes primary care records to identify patients showing signs of undiagnosed mental health conditions. The system has successfully identified over 60,000 patients needing mental health intervention who had not previously received such care, with 72% engaging in recommended treatment.
AI-powered therapeutic chatbots like Woebot and Wysa provide evidence-based cognitive behavioral therapy techniques through conversational interfaces. A Stanford University study found that college students using Woebot for two weeks experienced a 22% reduction in anxiety and depression symptoms compared to those given only informational resources.
At the University of Vermont Medical Center, natural language processing algorithms analyze speech patterns during routine telehealth appointments to detect subtle indicators of depression and suicidal ideation. This screening approach has increased identification of at-risk patients by 38% compared to standard questionnaire-based methods.
These AI mental health tools are particularly effective at reaching populations that traditionally underutilize mental health services. A study published in JAMA Psychiatry found that men and minority populations were 34% more likely to engage with AI-based mental health support than traditional therapy options, potentially helping address longstanding disparities in mental healthcare access.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations

While AI in healthcare offers tremendous benefits, its implementation comes with significant challenges that must be addressed. Data privacy remains a primary concern, as AI systems require access to sensitive patient information to function effectively. Healthcare organizations must implement robust security measures and transparent data governance policies to maintain patient trust.
Algorithmic bias presents another critical challenge. If AI systems are trained on datasets that underrepresent certain populations, they may perform less effectively for these groups, potentially exacerbating existing healthcare disparities. A study by the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association found that several commercial AI diagnostic systems showed performance disparities of up to 20% between demographic groups.
Regulatory frameworks are still evolving to address AI’s unique characteristics. The FDA has established a Digital Health Center of Excellence to develop appropriate oversight mechanisms for AI-based medical technologies, particularly those that continue to learn and adapt after deployment.
Healthcare professionals also face integration challenges as they incorporate AI tools into existing workflows. Effective implementation requires not just technological deployment but also organizational change management and appropriate training to ensure clinicians can use these tools effectively while maintaining their clinical judgment.
As AI continues to transform healthcare, ongoing dialogue between technologists, clinicians, ethicists, and patient advocates will be essential to ensure these powerful tools are deployed responsibly and equitably.
The Future of AI in Healthcare
The integration of artificial intelligence in healthcare represents one of the most significant technological transformations in modern medicine. As we’ve seen through these ten examples, AI is already delivering measurable improvements in diagnostic accuracy, treatment personalization, operational efficiency, and patient access across the United States healthcare system.
Looking ahead, we can expect AI applications to become increasingly sophisticated as they access larger datasets and benefit from advances in computing power. The convergence of AI with other technologies like genomics, wearable sensors, and 5G connectivity will likely create even more powerful tools for disease prevention, early intervention, and precision treatment.
For healthcare professionals, staying informed about these rapidly evolving technologies will be essential for providing optimal patient care. For patients, understanding AI’s capabilities and limitations can help them become more engaged partners in their healthcare journey.
As we navigate this technological revolution, maintaining a focus on the human elements of healthcare—empathy, communication, and ethical decision-making—will ensure that AI serves as a powerful tool for enhancing the healthcare experience rather than depersonalizing it.
Stay Updated on AI Healthcare Innovations
Want to keep pace with the latest developments in AI healthcare technology? Subscribe to our newsletter for quarterly updates on breakthrough applications, regulatory changes, and implementation best practices. Our expert-curated content helps healthcare professionals and technology enthusiasts stay at the forefront of this rapidly evolving field.







