In the rapidly evolving world of artificial intelligence, the most groundbreaking innovations often come from the strangest places. While tech giants pour billions into conventional AI development, creative thinkers are discovering unconventional applications that defy expectations. These unusual AI hacks—born from necessity, curiosity, or just plain weirdness—are proving that sometimes the oddest approaches yield the most impressive results.
What happens when you push AI tools beyond their intended purposes? When you combine them in ways their creators never imagined? Or apply them to industries that seem completely unrelated? The answers might surprise you. Let’s explore the bizarre yet brilliant world of unusual AI hacks that actually worked, and what they can teach us about thinking outside the algorithmic box.
The Art of Creative AI Misuse
The most fascinating unusual AI hacks often come from using tools in ways their creators never intended. These creative misuses demonstrate the flexibility of AI models and the ingenuity of human problem-solvers who see possibilities where others see limitations.
Case Study #1: Debugging Code with Image Generators
When software developer Mira Chen found herself stuck with a particularly stubborn bug in her code, she tried something that seemed completely illogical: she fed her code into DALL-E, an AI image generator designed to create pictures from text descriptions.
“I was desperate after spending 12 hours trying to find the issue,” Chen explains. “I thought maybe seeing my code represented visually might reveal patterns my brain wasn’t catching in text form.”
Surprisingly, it worked. The image generator created an abstract visualization that emphasized certain sections of the code through color and positioning. Chen immediately noticed an unusual pattern in the visualization that corresponded to a recursive function that was causing the bug.
“The AI had no idea it was helping me debug—it was just responding to patterns in the text. But seeing my code translated into visual patterns helped me spot the issue instantly,” she says.
Why This Hack Works: Image-generating AI models are trained to recognize patterns in data. When fed code instead of normal text descriptions, they still attempt to find and represent patterns—sometimes revealing structural issues that aren’t obvious when looking at the code directly.
Case Study #2: Farmers Using Chatbots for Crop Predictions
In rural Nebraska, a group of farmers with limited access to expensive agricultural technology found an unusual workaround: they began using ChatGPT to analyze weather patterns and predict optimal planting times.

Tom Whitaker, a third-generation farmer, started the trend: “We couldn’t afford the fancy predictive software that big agricultural corporations use. So I started feeding historical weather data, soil conditions, and crop yield information into ChatGPT, asking it to find patterns and make predictions.”
The results were surprisingly accurate. By creating detailed prompts that included decades of local farming data, the AI was able to suggest planting schedules that accounted for increasingly unpredictable weather patterns. Several farms reported yield increases of 15-20% after implementing the AI’s suggestions.
“It’s not perfect,” Whitaker admits, “but it’s giving small family farms access to analytical capabilities we couldn’t afford otherwise. We’re using a $20/month tool to compete with farms using $50,000 systems.”
“Sometimes the most powerful technology isn’t the most expensive—it’s the one you can adapt to solve your specific problem in unexpected ways.”
Case Study #3: The Spreadsheet-GPT Hybrid Monster
When marketing analyst Priya Sharma needed to analyze thousands of customer comments but couldn’t afford enterprise-level sentiment analysis software, she created what she calls “a hacky workaround that shouldn’t work but absolutely does.”
Sharma built a system that combined GPT-3 with Google Sheets through custom scripts. The system breaks down large datasets into smaller chunks that GPT can handle, processes them with specific analytical prompts, then reassembles the results in spreadsheets that automatically generate visualizations.
“Enterprise solutions would have cost us $30,000 annually,” Sharma explains. “Our hybrid system costs about $200 a month and actually gives us more flexibility because we can customize the prompts for different types of analysis.”
The system now processes over 50,000 customer comments monthly, categorizing sentiment, identifying emerging issues, and even generating response templates for the customer service team.
- Breaks large datasets into GPT-friendly chunks
- Uses custom prompts for different analytical needs
- Reassembles processed data in spreadsheets
- Automatically generates visualizations and reports
- Costs a fraction of enterprise solutions
Case Study #4: Teaching Language Models to “See” Through Text
Visually impaired developer Alex Morgan found an unusual way to “see” the world through AI. Unable to use image-recognition tools effectively, Morgan developed a technique to get detailed visual descriptions using only text-based language models.

“I created a system where I can input text descriptions of my surroundings from friends or basic object recognition, and the language model expands it into incredibly detailed spatial awareness information,” Morgan explains.
By crafting specialized prompts that ask the AI to “imagine” and describe spaces in extreme detail, Morgan receives rich contextual information about environments that basic object recognition might miss.
“Standard accessibility tools might tell me ‘chair, table, window,’ but my system describes the room layout, potential obstacles, and even suggests optimal navigation paths,” says Morgan. “It’s using a text-only AI to create a kind of virtual vision.”
Pro Tip: When using language models for unusual applications, the key is often in the prompt engineering. Be extremely specific about the format and type of information you need, and consider using “chain-of-thought” prompting where you ask the AI to reason through steps before giving its final output.
Case Study #5: AI Art Therapy for Non-Verbal Patients
At a rehabilitation center in Portland, therapist Dr. Eliza Wong discovered an unconventional application for AI art generators: helping non-verbal patients communicate complex emotions.

“We had a patient who had suffered a stroke and lost speech ability,” Wong explains. “Traditional art therapy was difficult because of limited motor control. We tried having him use simple text descriptions fed into an AI art generator, and suddenly he had a powerful way to express complex feelings.”
The approach has since expanded to help patients with various communication difficulties. Patients provide text descriptions or select from emotion words, and the AI generates images that represent their internal states. These images often reveal emotional nuances that might otherwise remain unexpressed.
“One patient generated an image that showed her depression as a glass wall between herself and others,” Wong notes. “It gave us a metaphor to work with that we might never have discovered through traditional communication methods.”
Case Study #6: Reverse-Engineering Music with Language Models
Independent music producer Jamal Williams developed a technique he calls “lyrical production” that uses language models in an unexpected way to create unique musical compositions.

“Instead of using AI to generate music directly, I feed detailed descriptions of emotions, scenes, and sound characteristics into GPT-4,” Williams explains. “The AI creates incredibly specific textual descriptions of musical elements that I then translate into actual compositions.”
Williams might prompt the AI with “Describe the exact sound texture, tempo changes, and instrument layering for a piece that evokes the feeling of reconciliation after conflict in a coastal setting.” The resulting detailed text description serves as a creative blueprint.
“It’s like having a hyper-articulate co-producer who can put into words the exact sonic qualities I’m trying to achieve,” says Williams. “I’ve created pieces using this method that I never would have conceived on my own.”
- Uses text descriptions instead of direct music generation
- Creates detailed “sonic blueprints” through language
- Translates textual descriptions into musical elements
- Combines human interpretation with AI suggestions
- Results in unique compositions beyond typical AI music
Case Study #7: Urban Planning with Gaming Engines and AI
A small city planning department with limited resources found an unusual solution to complex urban development challenges: they combined a gaming engine with AI to create interactive city models.
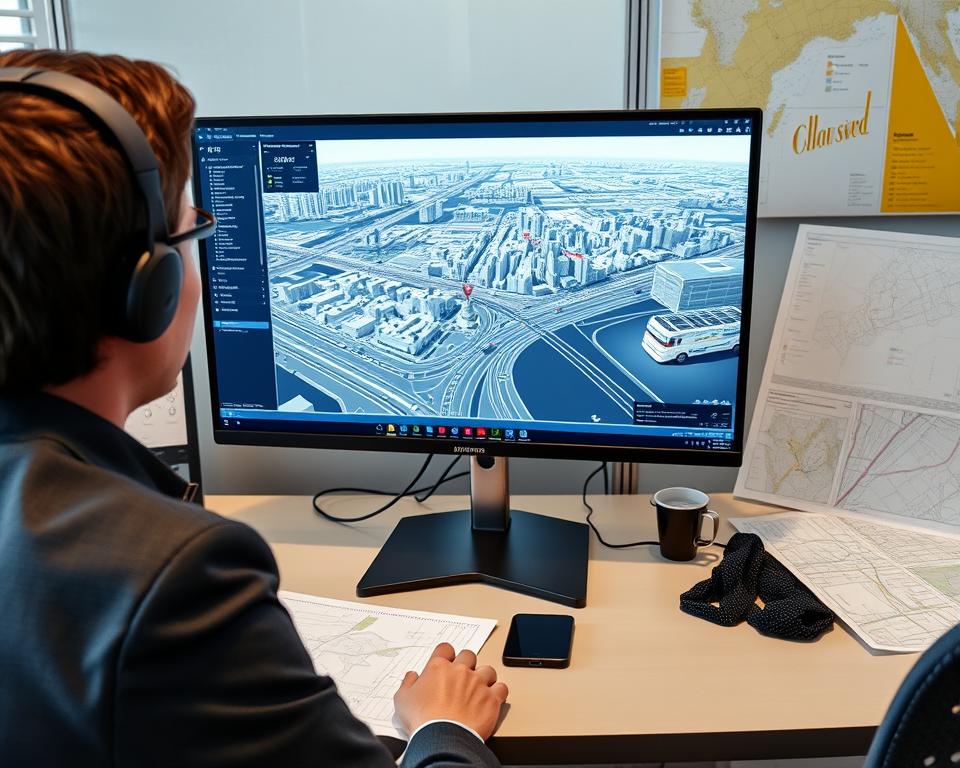

“We couldn’t afford specialized urban planning software that costs hundreds of thousands of dollars,” explains urban planner Marcus Chen. “So we built our city in a modified gaming engine and integrated AI to run simulations.”
The team used publicly available GIS data to create an accurate base model, then employed AI to generate and test thousands of development scenarios. The system simulates traffic patterns, pedestrian movement, environmental impacts, and even social dynamics.
“What makes this unusual is that we’re using tools designed for entertainment to solve serious civic problems,” Chen says. “The gaming engine gives us visualization capabilities that specialized planning tools lack, and the AI helps us identify optimal solutions from countless possibilities.”
Important Note: When repurposing AI tools for critical applications like urban planning or healthcare, always validate results against established methodologies. Unusual AI hacks can provide valuable insights, but should complement rather than replace proven approaches when public safety is involved.
Why These Unusual AI Hacks Worked
Despite their differences, these successful unusual AI applications share several common elements that contributed to their effectiveness:
Flexibility of Foundation Models
Many of these hacks leverage large foundation models (like GPT-4, DALL-E, etc.) that were trained on diverse data. This broad training makes them surprisingly adaptable to tasks beyond their intended use. They contain latent capabilities that creative users can unlock through clever prompting and application design.
Human-AI Collaboration
These successful hacks don’t rely on AI alone—they create effective human-AI partnerships. Humans provide the creative direction, domain expertise, and critical evaluation, while AI contributes processing power, pattern recognition, and generative capabilities. This collaboration leverages the strengths of both human and artificial intelligence.

Constraint-Driven Innovation
Many of these unusual AI hacks emerged from resource constraints—limited budgets, lack of specialized tools, or accessibility challenges. These constraints forced creative thinking and led to innovative applications that might never have emerged in resource-rich environments. The necessity truly became the mother of invention.
Domain Knowledge Transfer
These hacks often involve transferring AI capabilities from one domain to another—applying text generation to music production, or image creation to code debugging. This cross-domain application reveals new possibilities that specialized AI tools might miss because they’re optimized for narrower use cases.
Practical Takeaways: Creating Your Own Unusual AI Hacks
Inspired to create your own unusual AI applications? Here are actionable tips to help you think outside the conventional AI box:
Question Default Uses
Look at the AI tools you already use and ask: “What else could this do?” Don’t be limited by the intended purpose or official documentation. Experiment with using text generators for data analysis, image generators for pattern recognition, or voice assistants for process automation.
Combine Multiple AI Tools
Some of the most powerful unusual AI hacks come from connecting different AI systems. Try creating workflows where the output of one AI becomes the input for another, or build hybrid systems that leverage multiple AI capabilities simultaneously.
Start With Real Problems
The most useful unusual AI applications solve genuine problems. Identify pain points in your work or daily life that conventional solutions aren’t addressing effectively, then brainstorm how AI might help—even in non-obvious ways.
Practical Steps to Get Started
- Inventory available AI tools and their core capabilities
- List problems or inefficiencies in your work or personal life
- Brainstorm non-obvious connections between AI capabilities and your problems
- Start with small experiments that require minimal setup
- Document your process and results, even failures
- Iterate based on what you learn, refining your unusual approach
- Share your discoveries with others to get feedback and inspire new ideas
“The most exciting AI applications aren’t coming from billion-dollar research labs—they’re emerging from creative individuals who see possibilities where others see limitations.”
Prompt Engineering for Unusual Applications
Many unusual AI hacks rely on clever prompt engineering to coax AI systems into performing tasks they weren’t explicitly designed for. Here are some prompt techniques particularly useful for unusual applications:
Role Assignment
Ask the AI to adopt a specific role or perspective that aligns with your unusual use case. For example: “Act as a systems analyst examining this data for hidden patterns” or “Behave as a creative director evaluating these design options.”
Format Specification
Clearly define the output format you need, especially when it’s unusual. For example: “Analyze this text and output your findings as a JSON object with the following structure…” or “Present your analysis as a decision tree with exactly three levels.”
Balancing Creativity and Ethics in Unusual AI Applications
While experimenting with unusual AI applications can lead to breakthrough innovations, it’s important to consider the ethical implications of your hacks:
- Test thoroughly before deploying in critical contexts
- Be transparent about how AI is being used in your solution
- Consider potential unintended consequences
- Seek diverse perspectives on potential impacts
- Document limitations and edge cases
Responsible Innovation
- Using AI to circumvent safety measures
- Applying unusual hacks to high-risk decisions without validation
- Hiding the AI component from users or stakeholders
- Ignoring biases that might be amplified in unusual applications
- Failing to monitor outcomes for unexpected effects
Practices to Avoid
Remember that unusual applications may expose edge cases or behaviors that weren’t apparent in conventional use. This makes ongoing monitoring and evaluation particularly important when implementing creative AI hacks.

Conclusion: The Future of Unusual AI Hacks
The most transformative AI applications often emerge from unexpected places. As we’ve seen through these case studies, unusual AI hacks can solve problems that conventional approaches miss, create value from limited resources, and open new possibilities for human-AI collaboration.
The key to successful unusual AI applications isn’t just technical knowledge—it’s the willingness to experiment, the creativity to see new connections, and the persistence to refine unconventional approaches until they work. As AI tools become more accessible and flexible, the potential for unusual applications will only grow.
Whether you’re a developer, business professional, artist, or just someone curious about AI’s possibilities, there’s value in looking beyond the obvious uses. The next breakthrough AI application might not come from a research lab or tech giant—it might come from you, asking “What if?” and trying something that seems just strange enough to work.

Get Weekly Unusual AI Hacks
Join our newsletter to receive the strangest and most effective AI hacks delivered to your inbox every week. Be the first to discover unconventional applications that actually work!
Download Our Free Guide
Get our comprehensive guide to 50 Bizarre AI Applications That Actually Work. Learn how people are using AI in ways you never imagined!
Join Our AI Experimenters Community
Connect with others who are exploring unusual AI applications. Share your hacks, get feedback, and discover new possibilities!
Stay Updated on Unusual AI Innovations
Don’t miss out on the latest creative AI applications and unusual hacks. Subscribe to our newsletter for weekly updates, case studies, and practical tips.







