Beware: New Malware Scams Target Generative AI Users
In recent weeks, a surge of malware scams has been identified that specifically targets users of generative AI tools. Cybercriminals are impersonating the popular Kling AI platform to spread malicious software. A comprehensive investigation by Check Point Research (CPR) highlights how these scammers are leveraging deceptive tactics like fake social media ads and cloned websites to trick users into downloading harmful files.
What is Kling AI? An Overview
Kling AI is an innovative platform developed by Kuaishou, a prominent Chinese technology company, designed to generate videos from text prompts or images. Since its launch in June 2024, Kling AI has amassed over six million registered users, showcasing its rapid rise in popularity. Unfortunately, this success has also made it a prime target for cybercriminals eager to exploit its user base.
The Setup: Fake Ads and Deceptive Websites
The malware campaign commenced with sponsored Facebook ads promoting Kling AI. These ads led unsuspecting users to a meticulously crafted fake website that mirrored the authentic Kling AI interface. Once users landed on the site, they were prompted to upload an image and click “Generate” — a standard interaction for anyone familiar with generative tools.
However, users did not receive the expected AI-generated media. Instead, they were delivered a seemingly harmless downloadable file. Named something like Generated_Image_2025.jpg, complete with a standard image icon, this file was anything but innocent; it was a concealed executable, stealthily engineered to install malware on the user’s system.
 One of the fake malicious Kling AI ads (Credit: CPR)
One of the fake malicious Kling AI ads (Credit: CPR)
Unpacking the Malware: How It Operates
While specifics about the malware’s name and type remain largely unspecified, the initial phase of the attack utilized a technique called filename masquerading. By disguising a malicious file as a common media format, attackers increased the likelihood that users would open it. Once activated, the malware embedded itself within the system, reactivating every time the computer was powered on.
But that wasn’t the end of it. The true damage emerged in the second stage, which saw the deployment of a Remote Access Trojan (RAT) on the compromised systems. This malicious tool enabled the attackers to connect to an external command center, empowering them to monitor user activity, extract stored browser data, and even seize complete control of the system without the victim’s knowledge.
Stealth and Adaptation: Evolving Threats
Check Point’s findings indicate that each RAT variant utilized in this attack was slightly tweaked to elude detection by antivirus software. Some samples bore internal names like Kling AI Test Startup or date markers such as Kling AI 25/03/2025. This points to a sophisticated operation where the attackers actively tested and refined their methods, making them more adept at evading cybersecurity measures.
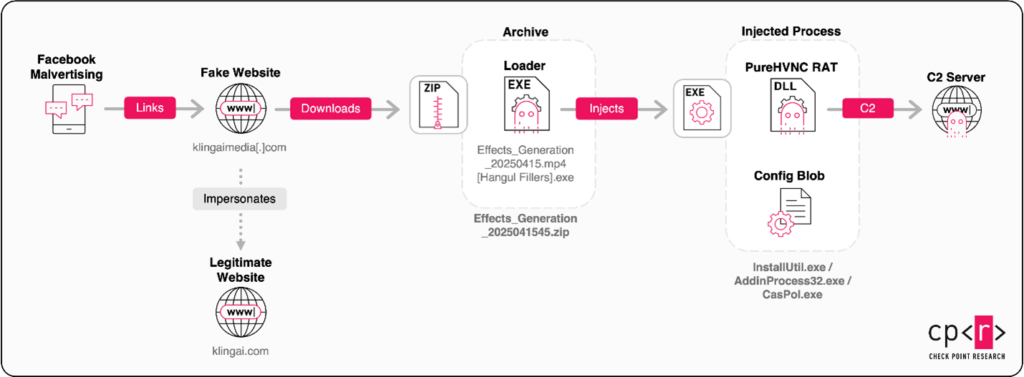
 Attack flow (Credit: CPR)
Attack flow (Credit: CPR)
Who’s Behind This Devious Scheme?
While the identity of the attackers remains under investigation, indicators suggest that this operation may be linked to cybercriminal groups based in Vietnam. Evidence includes the presence of Vietnamese-language debug strings within the malware and connections to previous campaigns that utilized Facebook for distributing malware.
Historically, cybercriminal organizations from this region have been linked to incidents involving deceptive ads and data-stealing malware on social media platforms. This latest scheme not only fits the existing patterns but also reflects the ongoing evolution of cyber threats that align with current digital trends.
Generative AI as a Target: The Rising Threat Landscape
The increasing popularity of generative AI tools provides a fertile ground for malicious actors. By replicating the authenticity of trusted services, these attackers prey on unsuspecting users. The polished appearance of fake websites further instills a false sense of security, leading individuals to assume that they are interacting with credible platforms.
Protecting Yourself: Tips for Users
In light of this emerging threat, CPR emphasizes the utmost importance of vigilance among users. Here are some actionable guidelines:
- Be Cautious of Sponsored Ads: Always scrutinize ads and verify their authenticity before clicking.
- Authenticate Websites: Ensure you are on the legitimate website before entering any personal information or downloading files.
- Stay Informed: Regularly educate yourself about current cyber threats and scams, particularly ones related to AI tools.
- Use Antivirus Software: Employ reliable antivirus and anti-malware programs to provide an additional layer of protection against malicious threats.
The Role of Social Media in Cyber Attacks
Social media platforms like Facebook can serve as both avenues for connection and vectors for exploitation. The deceptive ads seen in this campaign highlight the urgent need for better cybersecurity measures on social media platforms to protect users from scams.
Corporate Responsibility: A Call for Safe Practices
Kuaishou and other firms providing generative AI tools must take proactive measures to educate their users about potential scams and enhance their security protocols. Establishing clear communication channels for reporting suspicious activity will help safeguard the user base.
The Future of Cybersecurity: Ongoing Challenges
As the technological landscape evolves, so too do the threats that we face. IT security professionals must remain vigilant, constantly adapting to new attack vectors as cybercriminals become increasingly sophisticated. The battle against malware is ongoing, and collaboration across industries is vital.
The Bottom Line: Staying Safe Online
In this age of digital transformation, the threats are as intricate as the technologies themselves. Users must remain educated and cautious, particularly when interacting with popular platforms like Kling AI.
Conclusion: A Call to Action for Vigilance
The ongoing malware scams targeting users of generative AI tools underscore the necessity for constant vigilance and education. Users must question the legitimacy of online advertisements and ensure they employ robust protective measures. As cyber threats continue to evolve in complexity, staying informed about emerging risks is the first line of defense against potential attacks. With informed choices and a proactive stance, users can significantly bolster their cybersecurity posture and thwart the malicious intentions of cybercriminals.
source







