Cyber Threat UNC6032: A New Wave of AI-driven Malware
Rising Threat of AI Exploitation
In the evolving landscape of cybersecurity, the emergence of UNC6032, a sophisticated threat actor, has pivoted focus on the alarming misuse of AI technologies. Operating since mid-2024, UNC6032 exploits the popularity of legitimate AI video generation tools—specifically Luma, Canva, and Kling—to deploy malware-laden attacks.
How the Deceptive Campaign Works
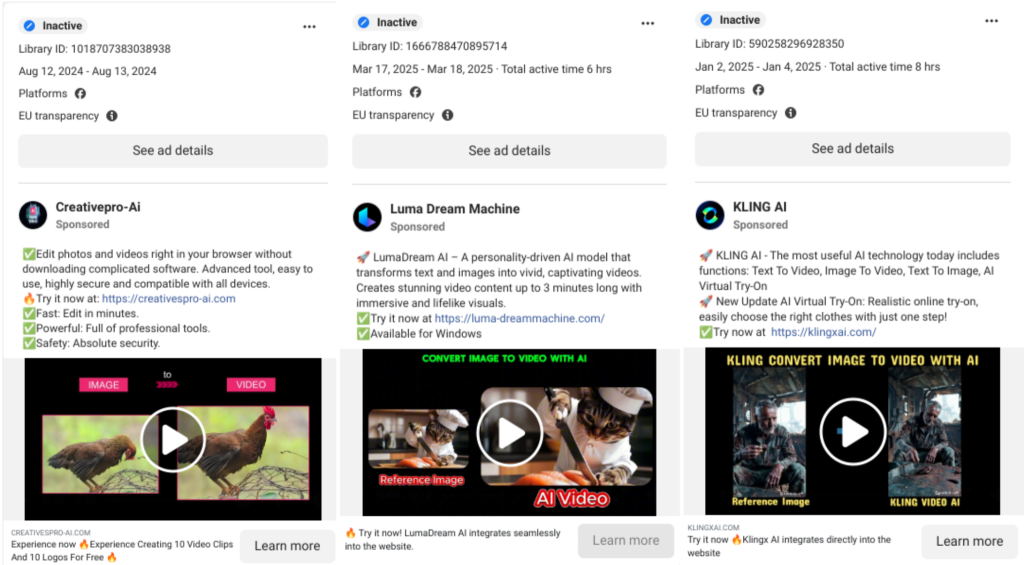
By leveraging engaging social media ads, UNC6032 directs unwitting victims toward counterfeit AI tool websites. These fraudsters have created enticing yet fake platforms that promise video generation, cleverly mimicking the interfaces of popular services like "Luma AI" and "Canva Dream Lab."
"Regardless of the prompts submitted by users, the outcome is always the same: an archive containing malware."
The result? Users receive a ZIP file heavy with malicious payloads—a well-structured tactic that goes largely unnoticed until it’s too late.
Insights from Cybersecurity Analysts
Recent analysis from Mandiant Threat Defense underscores the breadth of this campaign, indicating that these deceptive ads have reached millions across major platforms like Facebook and LinkedIn. Google’s Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG) suggests a possible Vietnam nexus for the UNC6032 group, raising concerns over its operational network’s potential.
Infection Chains and Malicious Payloads
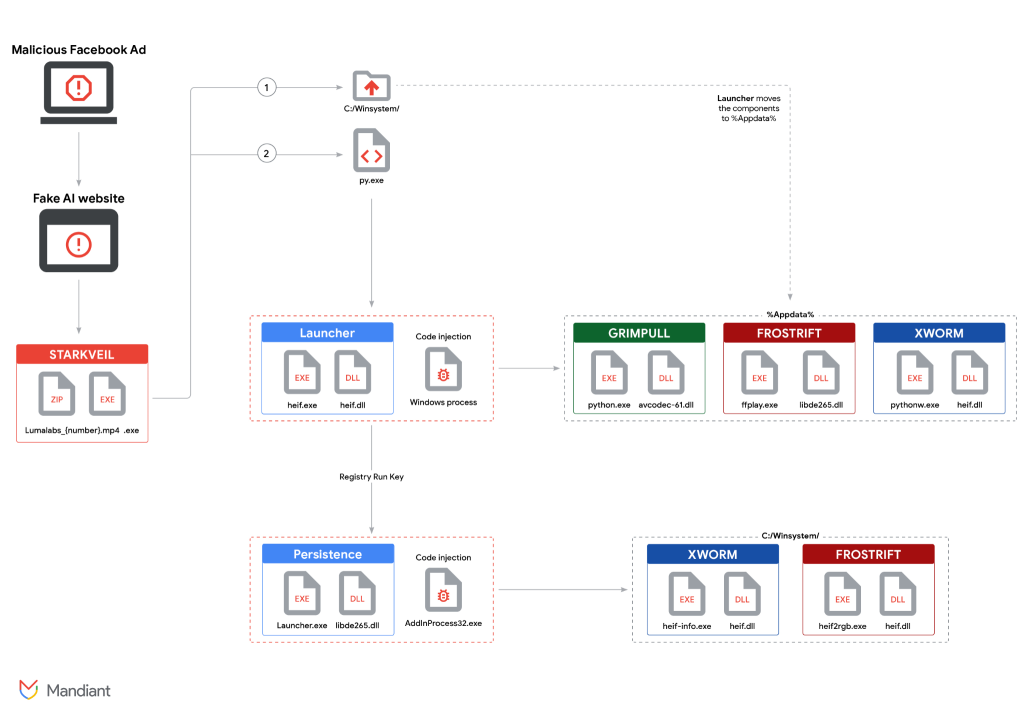
The technical sophistication of UNC6032 involves cleverly designed infection chains. Victims who upload any prompt to the fraudulent sites unwittingly download not just malware but specific threats named STARKVEIL, XWORM, and FROSTRIFT.
Malware Mechanics Explained
The primary malware, STARKVEIL, is notably Rust-coded, allowing it to effectively function as a dropper for further threats. It seamlessly implants additional payloads, including the dreaded XWORM and FROSTRIFT backdoors. The GRIMPULL downloader also makes an appearance, designed to harvest more sensitive information from the infected systems.
Persistence Tactics of UNC6032
The attackers have adopted a range of advanced persistence techniques involving DLL side-loading, in-memory droppers, and process injection. These strategies significantly complicate detection efforts for security products.
Exfiltration and Data Theft
Their malware modules are not just capable of basic infection; they also perform high-level reconnaissance activities. XWORM can conduct keylogging, scan for browser extensions, and identify host systems, while FROSTRIFT specializes in extracting sensitive data like login credentials, cookies, and valuable information from password managers and cryptocurrency wallets.
Data Transmission Channels
Stolen information is not just left to languish. Victims’ data is stealthily transmitted through encrypted channels such as Telegram and Tor, making recovery efforts considerably more complex.

The Reach of Malicious Ads
Stunningly, over 30 unique malicious domains have been identified, with some ads projecting their reach to more than 2.3 million users within the EU alone. This level of penetration highlights the urgency for improved vigilance in online security practices.
Rotating Domains for Extended Access
To outsmart detection algorithms, attackers frequently rotate their domains and launch short-lived ad campaigns. Both newly created and compromised Facebook accounts are employed, complicating response strategies. LinkedIn has also become a hotbed for these malicious endeavors, with domains like klingxai.com generating up to 250,000 ad impressions.
Meta’s Proactive Response
Fortunately, Mandiant commends Meta’s threat detection and response teams for their proactive measures in removing numerous malicious ads and suspicious domains. This collaborative effort showcases the significance of transparency initiatives like the Digital Services Act’s Ad Library, enabling better monitoring and action.
The Importance of User Vigilance
As these threats escalate in complexity and reach, end-users must remain vigilant and proactive in safeguarding their digital lives. Recognizing suspicious ads, employing security software, and understanding how to securely navigate suspected phishing attempts are essential steps in this modern age of cybersecurity.
The Future of Cybersecurity: A Call to Action
As cybercriminals increasingly weaponize foolproof systems to their advantage, the community must prioritize education about safe digital practices. Individual cybersecurity awareness is more important than ever, as small oversights can lead to significant vulnerabilities.
Towards a More Secure Digital Environment
Building a more secure online atmosphere involves ongoing innovation in cybersecurity solutions alongside consistent vigilance among users. As the industry continually evolves, so too must our strategies against these agile threat actors who exploit emerging technologies for malicious ends.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Battle Against Cyber Threats
The malicious activities of UNC6032 highlight a sobering reality in our increasingly digital world: cybersecurity threats are ever-evolving and require proactive participation from individuals and organizations alike. By fostering a collective awareness and response strategy, it becomes possible to mitigate risks and safeguard our technological ecosystem.
source







